Logistics Meaning in English
Logistics refers to the complete process of moving goods, from the place of one place to another. It involves coordinating various activities such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management to deliver goods at the right place at the right time and to the right customers.
Example:
- Logistics plays a vital role in getting food, medicines, clothes, electronics, and much more to the right place at the right time.
- FR8 is a reliable logistics company that offers a wide range of truck transport services
Logistics Meaning in Tamil
தளவாடங்கள்(Logistics) என்பது பொருட்களைத் தொடங்கும் இடத்திலிருந்து நுகர்வு இடத்திற்கு நகர்த்துவதற்கான முழுமையான செயல்முறையைக் குறிக்கிறது. இது போக்குவரத்து, மற்றும் சரக்கு மேலாண்மை போன்ற பல்வேறு நடவடிக்கைகளை ஒருங்கிணைத்து, சரியான இடத்தில் சரியான நேரத்தில் மற்றும் சரியான வாடிக்கையாளர்களுக்கு பொருட்களை வழங்குவதை உள்ளடக்குகிறது.
Example:
- உணவு, மருந்து, உடைகள், எலக்ட்ரானிக் பொருட்கள் போன்றவற்றை சரியான நேரத்தில் சரியான இடத்திற்கு கொண்டு செல்வதில் தளவாடங்கள் முக்கிய பங்கு வகிக்கின்றது.
- FR8 என்பது உங்கள் டிரக் போக்குவரத்து தேவைகளைப் பூர்த்தி செய்யும் ஒரு நம்பகமான தளவாட நிறுவனமாகும்.
Logistics Meaning in Hindi
लॉजिस्टिक्स से तात्पर्य माल को उत्पत्ति के स्थान से उपभोग के स्थान तक ले जाने की पूरी प्रक्रिया से है। इसमें सही समय पर और सही ग्राहकों तक सामान सही जगह पर पहुंचाने के लिए परिवहन, भंडारण और इन्वेंट्री प्रबंधन जैसी विभिन्न गतिविधियों का समन्वय करना शामिल है।
Example:
- FR8 एक भरोसेमंद लॉजिस्टिक्स कंपनी है जो ट्रक परिवहन सेवाओं की एक विस्तृत श्रृंखला प्रदान करती है
- FR8 भोजन, दवा, कपड़े, इलेक्ट्रॉनिक सामान और अन्य चीजों को सही समय पर सही जगह तक पहुंचाने में रसद महत्वपूर्ण
Logistics Meaning in Malayalam
ലോജിസ്റ്റിക്സ് എന്നത് ഉത്ഭവസ്ഥലത്ത് നിന്ന് ഉപഭോഗ സ്ഥലത്തേക്ക് ചരക്ക് നീക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള സമ്പൂർണ്ണ പ്രക്രിയയെ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. ശരിയായ സ്ഥലത്ത് ശരിയായ സമയത്ത് ശരിയായ ഉപഭോക്താക്കളിലേക്ക് സാധനങ്ങൾ എത്തിക്കുന്നതിന് ഗതാഗതം, വെയർഹൗസിംഗ്, ഇൻവെന്ററി മാനേജ്മെന്റ് തുടങ്ങിയ വിവിധ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളെ ഏകോപിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.
Example:
- ഭക്ഷണം, മരുന്നുകൾ, വസ്ത്രങ്ങൾ, ഇലക്ട്രോണിക്സ് സാധനങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയും മറ്റും ശരിയായ സ്ഥലത്ത് ശരിയായ സമയത്ത് എത്തിക്കുന്നതിൽ ലോജിസ്റ്റിക്സ് ഒരു പ്രധാന പങ്ക് വഹിക്കുന്നു.
- FR8 ട്രക്ക് ഗതാഗത സേവനങ്ങളുടെ വിശാലമായ ശ്രേണി വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു വിശ്വസനീയമായ ലോജിസ്റ്റിക് കമ്പനിയാണ്
Logistics Meaning in Telugu
లాజిస్టిక్స్ అనేది వస్తువులను మూలం నుండి వినియోగ ప్రదేశానికి తరలించే పూర్తి ప్రక్రియను సూచిస్తుంది. ఇది సరైన సమయంలో మరియు సరైన కస్టమర్లకు సరైన స్థలంలో వస్తువులను పంపిణీ చేయడానికి రవాణా, గిడ్డంగులు మరియు జాబితా నిర్వహణ వంటి వివిధ కార్యకలాపాలను సమన్వయం చేస్తుంది.
Example:
- ఆహారం, మందులు, బట్టలు, ఎలక్ట్రానిక్స్ మరియు మరెన్నో సరైన సమయంలో సరైన ప్రదేశానికి చేరుకోవడంలో లాజిస్టిక్స్ కీలక పాత్ర పోషిస్తుంది.
- FR8 అనేది విస్తృత శ్రేణి ట్రక్ రవాణా సేవలను అందించే విశ్వసనీయ లాజిస్టిక్స్ సంస్థ
Logistics Meaning in Marathi
लॉजिस्टिक म्हणजे माल हलविण्याच्या संपूर्ण प्रक्रियेस, मूळ ठिकाणापासून ते उपभोगाच्या ठिकाणी. यामध्ये वाहतूक, वेअरहाउसिंग आणि इन्व्हेंटरी मॅनेजमेंट यांसारख्या विविध क्रियाकलापांमध्ये समन्वय साधून योग्य वेळी योग्य ठिकाणी आणि योग्य ग्राहकांपर्यंत माल पोहोचवला जातो.
Example:
- अन्न, औषधे, कपडे, इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स आणि बरेच काही योग्य वेळी योग्य ठिकाणी मिळवण्यात लॉजिस्टिक महत्त्वाची भूमिका बजावते.
- FR8 ही एक विश्वासार्ह लॉजिस्टिक कंपनी आहे जी ट्रक वाहतूक सेवांची विस्तृत श्रेणी देते
Logistics Meaning in Kannada
ಲಾಜಿಸ್ಟಿಕ್ಸ್ ಮೂಲದ ಸ್ಥಳದಿಂದ ಬಳಕೆಯ ಸ್ಥಳಕ್ಕೆ ಸರಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಚಲಿಸುವ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಪ್ರಕ್ರಿಯೆಯನ್ನು ಸೂಚಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ಸರಿಯಾದ ಸಮಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಮತ್ತು ಸರಿಯಾದ ಗ್ರಾಹಕರಿಗೆ ಸರಿಯಾದ ಸ್ಥಳದಲ್ಲಿ ಸರಕುಗಳನ್ನು ತಲುಪಿಸಲು ಸಾರಿಗೆ, ಗೋದಾಮು ಮತ್ತು ದಾಸ್ತಾನು ನಿರ್ವಹಣೆಯಂತಹ ವಿವಿಧ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆಗಳನ್ನು ಸಂಯೋಜಿಸುವುದನ್ನು ಇದು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುತ್ತದೆ.
Example:
- ಆಹಾರ, ಔಷಧಿಗಳು, ಬಟ್ಟೆಗಳು, ಎಲೆಕ್ಟ್ರಾನಿಕ್ಸ್ ಮತ್ತು ಹೆಚ್ಚಿನದನ್ನು ಸರಿಯಾದ ಸಮಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಸರಿಯಾದ ಸ್ಥಳಕ್ಕೆ ತಲುಪಿಸುವಲ್ಲಿ ಲಾಜಿಸ್ಟಿಕ್ಸ್ ಪ್ರಮುಖ ಪಾತ್ರವನ್ನು ವಹಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
- FR8 ವ್ಯಾಪಕ ಶ್ರೇಣಿಯ ಟ್ರಕ್ ಸಾರಿಗೆ ಸೇವೆಗಳನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುವ ವಿಶ್ವಾಸಾರ್ಹ ಲಾಜಿಸ್ಟಿಕ್ಸ್ ಕಂಪನಿಯಾಗಿದೆ
The Role of Logistics
Planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and associated information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to fulfill customer needs is the responsibility of logistics management, a component of supply chain management.

Getting everything done in the supply chain as precisely as possible is the major objective of logistics management. All aspects of the supply chain must be considered by logistics management in order to attain this goal, including transportation, inventory, general warehousing, materials handling, cargo packaging, security, documentation, and information systems.
To guarantee that the finished product satisfies the customer’s needs in terms of quality, quantity, and timeliness, each of these components must be carefully planned and coordinated.
Different types of logistics
There are many different types of logistics, and the one utilized will depend on the sector and the particular requirements of the business. The following are some of the common ones:
1. Inbound Logistics
Getting products and supplies into a business is referred to as inbound logistics and is the first of many different types of logistics. To do this, all incoming supplies must be received, stored, and handled carefully.
A firm’s bottom line might be significantly impacted by inbound logistics, which is an important component of any organization that depends on tangible commodities. Customer satisfaction can be raised and expenditures can be decreased with proper inbound logistics management.
There are several forms of inbound logistics, each with their own special opportunities and drawbacks. These are the most typical forms of incoming logistics:
- Import Logistics
Import logistics means bringing different commodities and supplies into the company from outside the country. This procedure could be quite challenging since it calls for adherence to laws and rules associating to customs. - Inventory Management
The storage and tracking of all the incoming products is another responsibility of inbound logistics. Due to an efficient inventory management system, this can be done smoothly. - Warehousing
The storage of incoming commodities must be coordinated with inbound logistics. This can be a bit challenging because a strong warehousing system is needed. - Transportation
Transporting incoming commodities must be coordinated with inbound logistics as well. This could be difficult because a good transit system is needed.
2. Outbound logistics
Outbound logistics can be defined as the movement of products or finished goods from the production centers to the next supply chain link, and this can be done via various shipping methods, such as air, land, or sea.
Outbound logistics is the second type of logistics among different types of logistics. In this type, the products are transported from the warehouse to the point of consumption or the clients. To highlight this, order fulfillment is another name for outbound logistics.
3. Reverse logistics
Reverse Logistics can be defined as the transportation of goods or products from the end-users to the supply chain and is the third type of logistics among different types of logistics. When products need to be replaced or returned for refurbishing, repairing, exchanging, discarding, or recycling, reverse logistics is needed.
Reverse logistics is basically carried out after the sale is completed and is mostly preferred by the electronics and automobile industry, but is also used for products associated with other sectors.
For instance, you deliver a product that doesn’t fit the purpose, or is wrongly manufactured. You would have to send it back to the supplier for repair or replacement of the same. In scenarios like this, reverse logistics is required to get it done smoothly.
4. Third Party Logistics (3PL)
A third party logistics provider (3PL) can be defined as a business that outsources logistics services to clients. 3PLs provide a wide range of services, including shipping, warehousing, and logistics management.
In the supply chain for many companies, 3PLs are important. They could result in cheaper logistics costs and greater efficiency. 3PLs could provide access to new markets and talents quite oftenly.
3PLs come in a variety of forms. Some companies just specialize in one service, like shipping or warehousing. Whereas, some companies offer the whole scale of logistics services. There are 3PLs all over the world. While some are local service providers and some have a global reach.
5. Fourth Party Logistics (4PL)
4PL or fourth-party logistics is generally used by companies to outsource all of their logistics operations to a single logistics partner. The logistics provider would be in charge of overseeing the whole aspect of the client’s supply chain that includes evaluation, design, construction, management, and tracking.
For this very reason, a 4PL logistics partner signifies a greater level of supply chain management for the client.
6. Procurement Logistics
Procurement logistics can be referred to as sourcing materials/services required to manufacture a product. Procurement is the essential element in inbound logistics, and the scope depends on the size and nature of procurement needed by an organization.
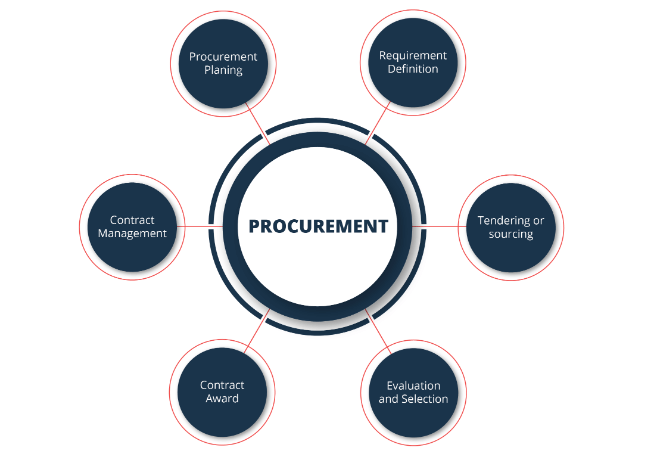
Procurement logistics targets to control supplies as per the requirement of the several operational processes of the organization. It generally includes monitoring quantities to be supplied, supply frequency, inventory management, demand forecasting, quality of service delivery, vendor selection, types of packing required, and mode of transportation required.
7. Manufacturing Logistics
Manufacturing logistics can be defined as the planning, coordination, and service tasks required to carry out production activities within a manufacturing space. It is basically organizing and managing the transportation, storage of materials and finished products within a manufacturing plant.
This also includes determining factors like when to shut down the manufacturing plant for maintenance, managing inventory levels, and meeting production schedules.
8.Distribution Logistics
Distribution logistics is also known as sales logistics or transport logistics and it deals with the movement of goods from manufacturer to customer. Customers can either be final customers or distributors in this process.
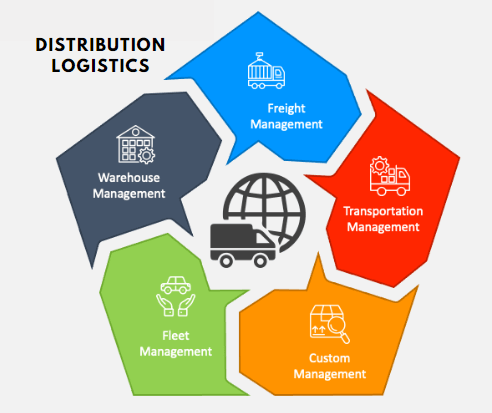
This logistics is the major driving force behind order fulfillment services. Supply chain management online courses enable professionals to learn precisely about the processes and methods to run a lean and smooth supply chain management.
Conclusion
These are the 6 major types of logistics that are being carried out by experienced companies to help meet the transportation and shipping requirements of businesses and manufacturers, through the supply chain.
So, if you are running a business that involves shipping and transportation of products to customers at their doorstep, you must pick the right logistics firm that can offer you diverse service aspects at nominal pricing and in the most efficient manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the seven roles in logistics?
Order processing, inventory management, warehousing, cargo handling, Transportation, monitoring, and delivery of goods at the right time.
- What are the types of logistics?
There are five types of logistics. They are: inbound logistics, outbound Logistics, third-Party logistics, fourth-party logistics, and Reverse logistics.
- What is logistics in supply management?
Logistics refers to the part of the supply chain that stores or distributes raw materials or finished products to the customer, who might be a producer, wholesaler, retailer, or end-user.